Venus - Landslide Deposits
Caption:
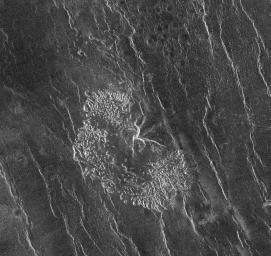
The Magellan spacecraft has observed remnant landslide deposits apparently resulting from the collapse of volcanic structures. This image, centered at 45.2 degrees south latitude, 201.4 degrees east longitude, shows a collapse deposit 70 kilometers (43 miles) across. The bright, highly textured deposit near the center of the image probably consists of huge blocks of fractured volcanic rock, many as large as several hundred meters across. A remnant of the volcano itself, about 20 kilometers (12.4 miles) across, is seen at the center of the image. The distorted radar appearance of the volcano is a result of extremely steep slopes on the 'scars' from which the landslide material originated. A field of numerous small volcanic domes can be seen in the northern half of the image. The bright irregular lineaments trending to the north-northwest are ridges caused by regional tectonic deformation of the upper layers of the Venusian crust.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name |
Value |
Additional Values |
| Target |
Venus |
|
| System |
|
|
| Target Type |
Planet |
|
| Mission |
Magellan |
|
| Instrument Host |
Magellan |
|
| Host Type |
Orbiter |
|
| Instrument |
Imaging Radar |
|
| Detector |
|
|
| Extra Keywords |
Grayscale, Radar, Volcano |
| Acquisition Date |
|
| Release Date |
1996-03-14 |
| Date in Caption |
|
|
| Image Credit |
NASA/JPL |
| Source |
photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00263 |
| Identifier |
PIA00263 |