|
Olympus Mons in Color
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (834 x 834) (35.0 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (834 x 834) (1.2 MB)
Caption:
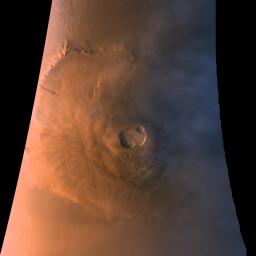
Sections of MOC images P024_01 and P024_02, shown here in color composite form, were acquired with the low resolution red and blue wide angle cameras over a 5 minute period starting when Mars Global Surveyor was at its closest point to the planet at the beginning of its 24th orbit (around 4:00 AM PDT on October 20, 1997). To make this image, a third component (green) was synthesized from the red and blue images. During the imaging period, the camera was pointed straight down towards the martian surface, 176 km (109 miles) below the spacecraft. During the time it took to acquire the image, the spacecraft rose to an altitude of 310 km (193 miles). Owing to data camera scanning rate and data volume constraints, the image was acquired at a resolution of roughly 1 km (0.609 mile) per pixel. The image shown here covers an area from 12° to 26° N latitude and 126° N to 138° W longitude. The image is oriented with north to the top.
As has been noted in other MOC releases, Olympus Mons is the largest of the major Tharsis volcanoes, rising 25 km (15.5 miles) and stretching over nearly 550 km (340 miles) east-west. The summit caldera, a composite of as many as seven roughly circular collapse depressions, is 66 by 83 km (41 by 52 miles) across. Also seen in this image are water-ice clouds that accumulate around and above the volcano during the late afternoon (at the time the image was acquired, the summit was at 5:30 PM local solar time). To understand the value of orbital observations, compare this image with the two taken during approach ( PIA00929 and PIA00936 ), that are representative of the best resolution from Earth.
Through Monday, October 28, the MOC had acquired a total of 132 images, most of which were at low sun elevation angles. Of these images, 74 were taken with the high resolution narrow angle camera and 58 with the low resolution wide angle cameras. Twenty-eight narrow angle and 24 wide angle images were taken after the suspension of aerobraking. These images, including the one shown above, are among the best returned so far.
Background Info:
Launched on November 7, 1996, Mars Global Surveyor entered Mars orbit on Thursday, September 11, 1997. The original mission plan called for using friction with the planet's atmosphere to reduce the orbital energy, leading to a two-year mapping mission from close, circular orbit (beginning in March 1998). Owing to difficulties with one of the two solar panels, aerobraking was suspended in mid-October and is scheduled to resume in mid-November. Many of the original objectives of the mission, and in particular those of the camera, are likely to be accomplished as the mission progresses.
Malin Space Science Systems and the California Institute of Technology built the MOC using spare hardware from the Mars Observer mission. MSSS operates the camera from its facilities in San Diego, CA. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Mars Surveyor Operations Project operates the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft with its industrial partner, Lockheed Martin Astronautics, from facilities in Pasadena, CA and Denver, CO.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Global Surveyor | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Atmosphere, Color, Dust, Mountain, Volcano, Water | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 1998-04-23 | |
| Date in Caption | 1997-10-20 | |
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL/Malin Space Science Systems | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00993 | |
| Identifier | PIA00993 | |
