|
Eros in Stereo
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (670 x 416) (21.9 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (670 x 416) (247.8 kB)
Caption:
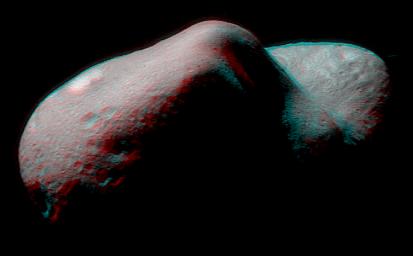
Stereo imaging will be an important tool on NEAR for geologic analysis of Eros, because it provides three-dimensional information on the asteroid's landforms and structures. This anaglyph can be viewed using red-blue glasses to show Eros in stereo. It was constructed from images taken on February 14 and 15 that showed the same part of Eros from two slightly different viewing perspectives. The smallest feature visible is 100 feet (30 meters) across. For this image the spacecraft position was not optimum for stereo, but it will improve over the next few days allowing better 3-D views.
Background Info:
Built and managed by The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, Maryland, NEAR was the first spacecraft launched in NASA's Discovery Program of low-cost, small-scale planetary missions. See the NEAR web page at http://near.jhuapl.edu/ for more details.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | 433 Eros | |
| System | Near Earth Objects | |
| Target Type | Asteroid | |
| Mission | NEAR Shoemaker | |
| Instrument Host | NEAR Shoemaker | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | Multi-Spectral Imager (MSI) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2000-05-07 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL/JHUAPL | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02471 | |
| Identifier | PIA02471 | |
