|
Comparison of Martian Radiation Environment with International Space Station
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (907 x 621) (79.4 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (907 x 621) (315.0 kB)
Caption:
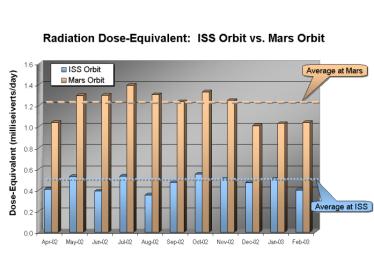
This graphic shows the radiation dose equivalent as measured by Odyssey's Martian radiation environment experiment at Mars and by instruments aboard the International Space Station, for the 11-month period from April 2002 through February 2003. The accumulated total in Mars orbit is about two and a half times larger than that aboard the Space Station. Averaged over this time period, about 10 percent of the dose equivalent at Mars is due to solar particles, although a 30 percent contribution from solar particles was seen in July 2002, when the sun was particularly active.
Background Info:
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the 2001 Mars Odyssey mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, D.C. The radiation experiment was provided by the Johnson Space Center, Houston, Tex. Lockheed Martin Astronautics, Denver, Colo., is the prime contractor for the project, and developed and built the orbiter. Mission operations are conducted jointly from Lockheed Martin and from JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | 2001 Mars Odyssey | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Odyssey | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2003-03-13 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL/JSC | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04258 | |
| Identifier | PIA04258 | |
