|
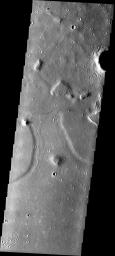
Channel to Nowhere
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (1421 x 3177) (849.4 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (1421 x 3177) (3.8 MB)
Caption:
Released 22 May 2003
A channel-like feature roughly halfway between the Isidis Basin and Elysium Mons shows no connection to either a source region or terminal basin. It may be that this feature is not a channel at all and has instead arisen from the erosion of a once continuous layer of material into remnants that mimic a channel.
Image information: VIS instrument. Latitude 20.9, Longitude 105 East (255) meter/pixel resolution.
Note: this THEMIS visual image has not been radiometrically nor geometrically calibrated for this preliminary release. An empirical correction has been performed to remove instrumental effects. A linear shift has been applied in the cross-track and down-track direction to approximate spacecraft and planetary motion. Fully calibrated and geometrically projected images will be released through the Planetary Data System in accordance with Project policies at a later time.
Background Info:
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the 2001 Mars Odyssey mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, D.C. The Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) was developed by Arizona State University, Tempe, in collaboration with Raytheon Santa Barbara Remote Sensing. The THEMIS investigation is led by Dr. Philip Christensen at Arizona State University. Lockheed Martin Astronautics, Denver, is the prime contractor for the Odyssey project, and developed and built the orbiter. Mission operations are conducted jointly from Lockheed Martin and from JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | 2001 Mars Odyssey | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Odyssey | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Grayscale, Mountain, Thermal | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2003-05-26 | |
| Date in Caption | 2003-05-22 | |
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL/Arizona State University | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04537 | |
| Identifier | PIA04537 | |
