|
Layered Deposits in Terby
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (2048 x 2717) (620.0 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (2048 x 2717) (5.6 MB)
Caption:
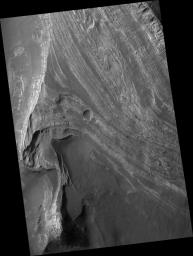
Terby Crater is a large (diameter ~165 km), Noachian-aged crater located on the northern rim of the Hellas impact basin (28°S, 74.1°E).
Terby hosts a very impressive sequence of predominantly light-toned layered deposits, up to 2.5 km thick that are banked along its northern rim and extend toward the center of the crater.
This image shows a stack of layered rocks as they are exposed westward facing scarp. The layered sequence consists of many beds that are repetitive, relatively horizontal and laterally continuous on a kilometer scale. Many beds are strongly jointed and fractured and exhibit evidence of small-scale wind scour.
The light-toned layers are typically at least partially covered with dark mantling material that obscures the layers as well as debris and numerous, meter-scale boulders that have cascaded down slope. The processes responsible for formation of these layers remain a mystery, but could include deposition in water, by the wind, or even volcanic activity.
This HiRISE image is a proposed landing site for the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) in Terby Crater.
Observation Geometry
Image
PSP_001662_1520
was taken by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera onboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft on 03-Dec-2006. The complete image is centered at -27.6 degrees latitude, 74.2 degrees East longitude. The range to the target site was 258.1 km (161.3 miles). At this distance the image scale is 25.8 cm/pixel (with 1 x 1 binning) so objects ~77 cm across are resolved. The image shown here has been map-projected to 25 cm/pixel and north is up. The image was taken at a local Mars time of 03:40 PM and the scene is illuminated from the west with a solar incidence angle of 68 degrees, thus the sun was about 22 degrees above the horizon. At a solar longitude of 144.9 degrees, the season on Mars is Northern Summer.
Background Info:
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, is the prime contractor for the project and built the spacecraft. The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is operated by the University of Arizona, Tucson, and the instrument was built by Ball Aerospace and Technology Corp., Boulder, Colo.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | Curiosity Rover |
| Host Type | Orbiter | Rover |
| Instrument | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Crater, Grayscale, Impact, Map, Volcano, Water | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2007-01-24 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL/Univ. of Arizona | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09575 | |
| Identifier | PIA09575 | |
