|
First X-ray View of Martian Soil
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (582 x 600) (157.3 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (582 x 600) (351.3 kB)
Caption:
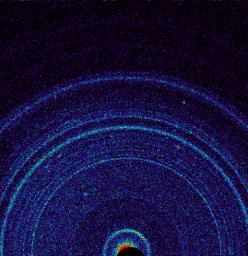
This graphic shows results of the first analysis of Martian soil by the Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin) experiment on NASA's Curiosity rover. The image reveals the presence of crystalline feldspar, pyroxenes and olivine mixed with some amorphous (non-crystalline) material. The soil sample, taken from a wind-blown deposit called "Rocknest" within Gale Crater, where the rover landed, is similar to volcanic soils in Hawaii.
Curiosity scooped the soil on Oct. 15, 2012, the 69th sol, or Martian day, of operations. It was delivered to CheMin for X-ray diffraction analysis on October 17, 2012, the 71st sol. By directing an X-ray beam at a sample and recording how X-rays are scattered by the sample at an atomic level, the instrument can definitively identify and quantify minerals on Mars for the first time. Each mineral has a unique pattern of rings, or "fingerprint," revealing its presence. The colors in the graphic represent the intensity of the X-rays, with red being the most intense.
Background Info:
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, manages the project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, and built Curiosity and CheMin.
For more information about Curiosity and its mission, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/msl and http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) | |
| Instrument Host | Curiosity Rover | |
| Host Type | Rover | |
| Instrument | Chemistry & Mineralogy X-Ray Diffraction (CheMin) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Crater, Volcano | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2012-10-30 | |
| Date in Caption | 2012-10-15 | 2012-10-17 |
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ames | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA16217 | |
| Identifier | PIA16217 | |
