|
Inspecting Soils Across Mars
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (1600 x 1200) (141.9 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (1600 x 1200) (5.8 MB)
Caption:
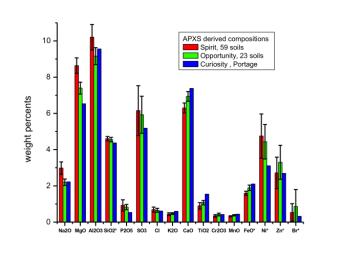
This graph compares the elemental composition of typical soils at three landing regions on Mars: Gusev Crater, where NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Spirit traveled; Meridiani Planum, where Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity still roams; and now Gale Crater, where NASA's newest Curiosity rover is currently investigating. The data from the Mars Exploration Rovers are from several batches of soil, while the Curiosity data are from soil taken inside a wheel scuff mark called "Portage" and examined with its Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS).
These early results indicate that the samples investigated by Curiosity are very similar to those at previous landing sites.
Error bars indicate the variations for the given number of soils measured for the Mars Exploration Rovers along the traverse. Note that concentrations of silicon dioxide and iron oxide were divided by 10, and nickel, zinc and bromine levels were multiplied by 100.
Background Info:
JPL manages the Mars Science Laboratory/Curiosity for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The rover was designed, developed and assembled at JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
For more about NASA's Curiosity mission, visit: http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/msl , http://www.nasa.gov/mars , and http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) | Mars Exploration Rover (MER) |
| Instrument Host | Curiosity Rover | Opportunity (MER-B), Spirit (MER-A) |
| Host Type | Rover | |
| Instrument | Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer (APXS) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Crater | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2012-12-03 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Guelph | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA16572 | |
| Identifier | PIA16572 | |
