|
Chlorinated Compounds at ‘Rocknest’
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (1600 x 1200) (253.8 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (1600 x 1200) (5.8 MB)
Caption:
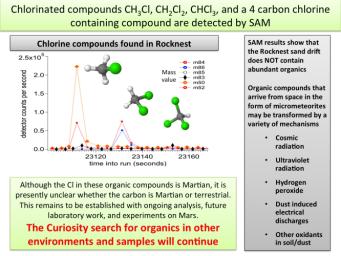
The first examinations of Martian soil by the Sample Analysis at Mars, or SAM, instrument on NASA's Mars Curiosity rover show no definitive detection of Martian organic molecules at this point. Organic molecules are carbon-containing compounds essential for life on Earth. The soil grains were acquired from a wind drift named "Rocknest."
The instrument did detect simple chlorinated carbon compounds, represented by ball and stick models on the graph. These compounds contain hydrogen and carbon as well as chlorine. More work is needed to determine if the carbon in these molecules is of terrestrial or Martian origin. The chlorinated compounds were likely created from a reaction with perchlorate or a perchlorite-like phase and carbon-containing molecules.
Future experiments will further address the question of the observed carbon's origins, and the rover will continue to search for organics in both rocks and sands in other environments of Gale Crater.
Background Info:
JPL manages the Mars Science Laboratory/Curiosity for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The rover was designed, developed and assembled at JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
For more about NASA's Curiosity mission, visit: http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/msl , http://www.nasa.gov/mars , and http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) | |
| Instrument Host | Curiosity Rover | |
| Host Type | Rover | |
| Instrument | Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Crater | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2012-12-03 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/GSFC | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA16576 | |
| Identifier | PIA16576 | |
