|
Argon Isotopes Provide Robust Signature of Atmospheric Loss
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (960 x 720) (65.2 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (960 x 720) (2.1 MB)
Caption:
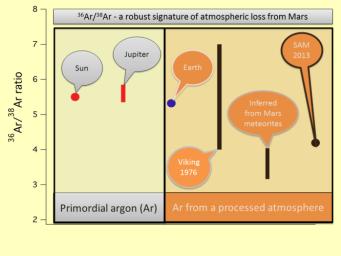
This image shows the ratio of the argon isotope argon-36 to the heavier argon isotope argon-38, in various measurements. The point farthest to the right designates a new (2013) measurement of the ratio in the atmosphere of Mars, made by the quadrupole mass spectrometer in the Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) suite of instruments in NASA's Curiosity Mars rover. For comparison, the previous measurement at Mars by the Mars Viking project in 1976 is shown also. The SAM result is at the lower end of the range of uncertainty of the Viking data, but compares well with ratios of argon istotopes from some Mars meteorites. The value determined by SAM is significantly lower than the value in the sun, Jupiter and Earth, which implies loss of the lighter isotope compared to the heavier isotope over geologic time. The argon isotope fractionation provides clear evidence of the loss of atmosphere from Mars.
Background Info:
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project and the mission's Curiosity rover for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The rover was designed and assembled at JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
More information about Curiosity is online at http://www.nasa.gov/msl and http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl/ .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) | Viking |
| Instrument Host | Curiosity Rover | |
| Host Type | Rover | |
| Instrument | Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Atmosphere, Color | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2013-04-08 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA16818 | |
| Identifier | PIA16818 | |
