|
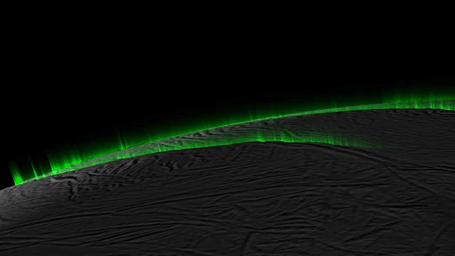
Icy Curtain Eruptions on Enceladus Create an Illusion of Discrete Jets (Simulation)
- Click the image above for a larger view
 Movie Download Options
Movie Download Options- Full-Res JPEG (1278 x 719) (54.0 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (1278 x 719) (2.8 MB)
Caption:
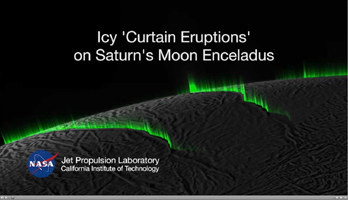
Click on the image for the animation
Recent research suggests much of the eruption activity on the surface of Saturn's moon Enceladus could be in the form of broad, curtain-like eruptions, rather than discrete jets.
This simulation, which begins and ends with a real image from NASA's Cassini spacecraft, demonstrates how the appearance of discrete jets could be an optical illusion that varies based on viewing geometry. As the perspective rotates around Enceladus' south pole, "phantom" jets seem to appear and disappear.
The researchers involved in the study think some prominent jets likely are what they appear to be -- meaning individual, discrete sources -- but most of the activity seen in the images can be explained as curtain eruptions.
See PIA19061 for a related image.
Background Info:
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov and http://www.nasa.gov/cassini . The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Enceladus | |
| System | Saturn | |
| Target Type | Satellite | |
| Mission | Cassini-Huygens | |
| Instrument Host | Cassini Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | Imaging Science Subsystem (ISS) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Movie, Rotation | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2015-05-06 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI/PSI | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19060 | |
| Identifier | PIA19060 | |
