
|
Night Vision
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (2880 x 1800) (985.4 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (2880 x 1800) (5.2 MB)
Caption:
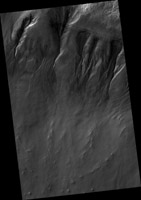
Map Projected Browse Image
Click on the image for larger version
It's hard to see in the dark. Most HiRISE images are are taken when the sun is at least 15 degrees above the horizon. (If you hold your hand at arm's length with fingers together, it's about five degrees wide on average.) However, to see what's going on in winter, we need to look at times and places where the Sun is just barely over the horizon.
This image was taken to look at seasonal frost in gullies during southern winter on Mars, with the Sun only about two degrees over the horizon (just before sunset). To make things more difficult, the gullies are on a steep slope facing away from the sun, so they are in deep shadow. Under these conditions, HiRISE takes what are called "bin 4" images. This means that the image shows less detail, but by adding up the light from 16 pixels (a 4x4 square) we can see details in shadows.
Even with the reduced resolution, we can see plenty of detail in the gullies, and learn about the seasonal frost.
Background Info:
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colo. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Grayscale, Map, Shadow | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2016-03-10 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20480 | |
| Identifier | PIA20480 | |
