|
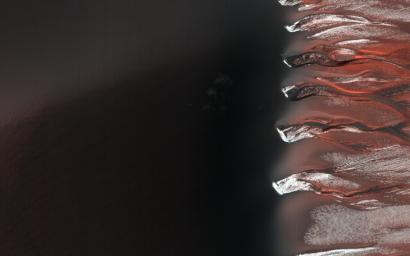
Frosty Alcoves on Kaiser Crater Dunes
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (2880 x 1800) (549.2 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (2880 x 1800) (12.9 MB)
Caption:

Map Projected Browse Image
Click on the image for larger version
Kaiser Crater hosts a large field of sand dunes. Every winter the dunes are covered with a layer of seasonal carbon dioxide ice (dry ice). In early spring the ice begins to sublimate (going directly from solid ice to gas).
In this image, the dunes are partially free of seasonal ice, with the contrast making it easy to see the ripples. Deep alcoves have been carved at the crest of the dune. We hypothesize that this is the result of the gas coming from the dry ice, destabilizing the sand at the crest. As blocks of ice protected in the cold shadows of the alcove break off they slide downslope, carving the channels we see.
Background Info:
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colo. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Crater, Dune, Map, Shadow | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2016-09-08 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21038 | |
| Identifier | PIA21038 | |
