|
Now and Long Ago at Gale Crater, Mars (Illustration)
- Click the image above for a larger view
 Movie Download Options
Movie Download Options- Full-Res JPEG (1920 x 1080) (77.5 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (1920 x 1080) (491.6 kB)
Caption:
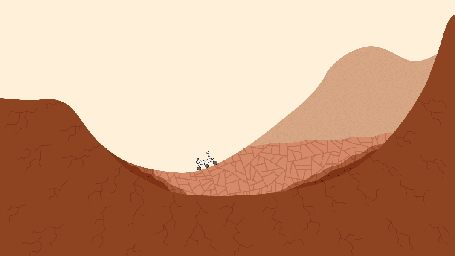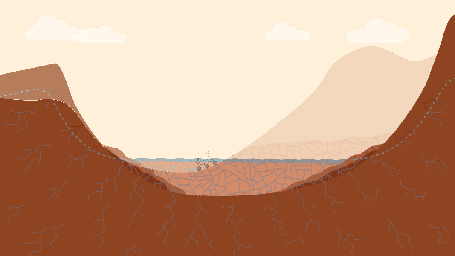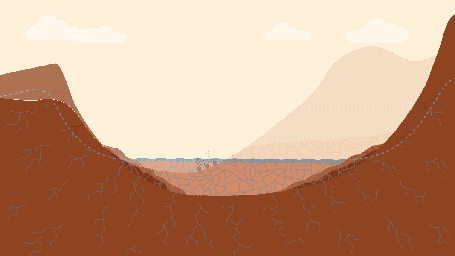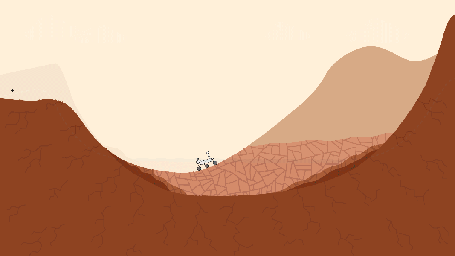
This pair of drawings depicts the same location on Mars at two points in time: now and billions of years ago. The location is in Gale Crater, near the Red Planet's equator. Since August 2012, NASA's Curiosity Mars rover mission has been investigating rock layers in the crater floor and in the crater's central peak (Mount Sharp) for information recorded in the rocks about ancient environmental conditions and how they changed over time.
Slide 1 shows a present-day snapshot of the northern half of Gale Crater. North is to the left. The underlying basement is the crust of Mars that forms the crater's rim (left) and central peak (right). About 3.5 billion years ago, rivers brought sediment into the crater, depositing pebbles where the river was flowing more quickly, sand where the river entered a standing body of water in the center of the basin, and silt within this lake. Lake level rose over time as the sediments built up. Eventually they were buried by dry dust. These sediments later turned into the conglomerate, sandstone, mudstone, and duststone rocks that Curiosity has found. Wind then carved the stack of deposits into the present shape of a mountain, which Curiosity is climbing as approximately shown. The basement rock fractured during the initial impact that formed the crater, and the later sediments fractured as they were buried.
Slide 2 shows a snapshot in time when a lake was present in the crater. As on Earth, Martian lakes were the surface expression of a much larger lake and groundwater system. Spaces between grains and in fractures were saturated with water at levels below the water table (dashed blue line). This groundwater circulated due to gravity and the topography within and around the crater. In this case, groundwater pressurized under the nearby Martian highlands may have flowed into the crater, where it would be less confined. Groundwater also flowed downward from the lake. As the groundwater circulated, it drove chemical reactions that dissolved some minerals and precipitate others. Habitable environments in ancient Gale Crater -- identified during Curiosity's first year on Mars --expanded both in space and time beyond just the lakes. They extend throughout the subsurface where groundwater was present, and extended in time well after the lakes disappeared, when groundwater continued to circulate through the buried and fractured sediments.
Presented at the 2016 AGU Fall Meeting on Dec. 13. in San Francisco, CA.
Background Info:
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
For more information about Curiosity, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl and http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) | |
| Instrument Host | Curiosity Rover | |
| Host Type | Rover | |
| Instrument | ||
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Crater, Dust, Impact, Mountain, Movie, Water | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2016-12-13 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21255 | |
| Identifier | PIA21255 | |
