
|
A Window into the Past
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (2880 x 1800) (891.8 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (2880 x 1800) (15.4 MB)
Caption:
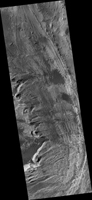
Map Projected Browse Image
Click on the image for larger version
The layered sedimentary deposits inside the giant canyons of Mars have puzzled scientists for decades. These light toned deposits have fine, horizontal laminations that are unlike the rugged rim rock of the Valles Marineris as seen by NASA’s Mars Reconnaisance Orbiter (MRO).
Various ideas for the origin of the layered sediments have suggested lake deposits, wind blown dust and sand, or volcanic materials that erupted after the canyon was formed, and possibly filled with water.
One particular layered deposit, called Ceti Mensa, attracted attention because its deep red color in images collected by the Viking Orbiter mission during the 1970s. Located in west Candor Chasma in the north of the Valles Marineris, Ceti Mensa is an undulating plateau that rises 3 kilometers above the canyon floor and is bounded by steep scarps up to 1.5 kilometers in height. Deep red hues are on the west-facing scarp in particular. The red tint may be due to the presence of crystalline ferric oxide, suggesting that the material may have been exposed to heat or water, or both.
Spectral measurements by the Mars Express OMEGA and MRO CRISM instruments confirm the presence of hydrated sulfate salts, such as gypsum and kieserite . These minerals are important for two reasons. On Earth, they typically form in wet environments, suggesting that the deposits in Ceti Mensa may have formed under water. On Mars, these deposits could be valuable to future Martian colonists as fertilizer for growing crops.
In a view of the colorful west-facing scarp of Ceti Mensa, we see the interior layers of the deposit, giving us a window into the past history of the sediments as they accumulated over time. We also see layers that were previously too small to view, and a surface that is thoroughly fractured, eroded into knobs, and partially covered by young dark sand dunes.
This is a stereo pair with ESP_051986_1750 .
The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 26.7 centimeters (10.5 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 80 centimeters (31.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up.
Background Info:
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colo. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | Mariner, Mars Express, Mars Express (MEX), Viking |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | Mars Express, Mars Express Orbiter |
| Host Type | Orbiter | Flyby Spacecraft |
| Instrument | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) | Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM), Visible and Infrared Mineralogical Mapping Spectrometer (OMEGA) |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Dune, Dust, Map, Volcano, Water | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2017-10-23 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22051 | |
| Identifier | PIA22051 | |
