
|
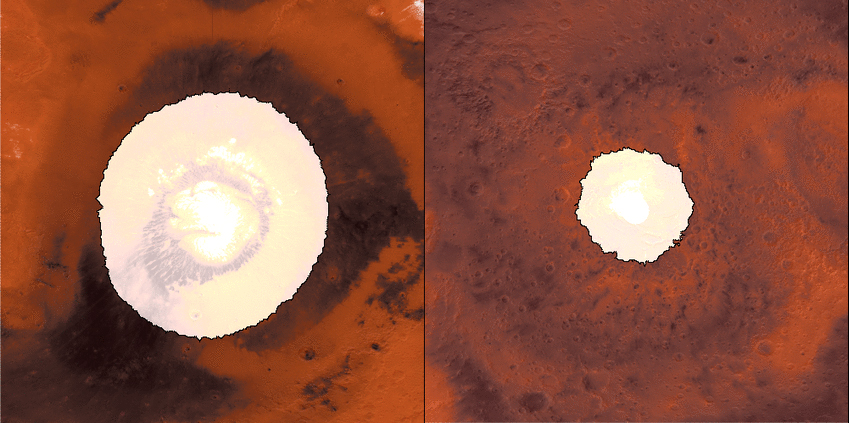
Growth and Retreat of the CO2 Ice at the Martian Poles
- Click the image above for a larger view
 Movie Download Options
Movie Download Options- Full-Res JPEG (849 x 423) (383.2 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (849 x 423) (562.4 kB)
Caption:
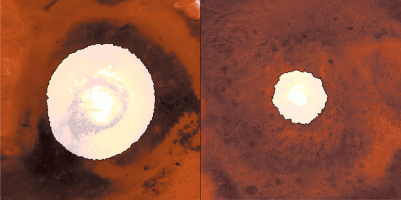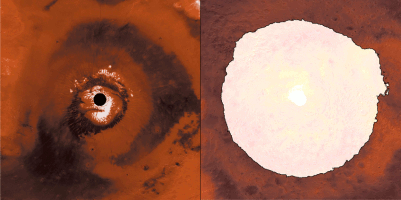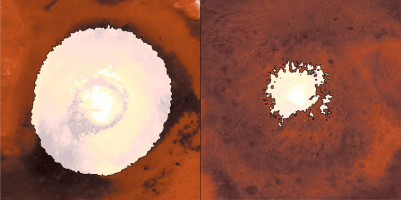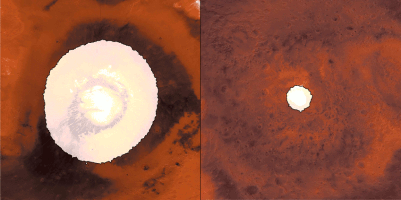
Click for larger animation
This animation shows a side-by-side comparison of CO
As Mars enters fall and winter, reduced sunlight allows CO
How do spacecraft observe the Martian surface in the polar night, when the Sun is below the horizon for weeks or even months, or in the spring, when it's hazy? They use infrared instruments measuring surface temperatures, even when the ground is in complete darkness or the atmosphere obscured. CO
Each panel of the animation is about 3,728 miles (6,000 kilometers) across. This data was collected by the Mars Climate Sounder (MCS) instrument on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, and the Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) onboard NASA's now defunct Mars Global Surveyor. The MCS data was collected between mid-2006 and the end of 2013; the TES data was collected between early 1999 to late 2006.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | Mars Global Surveyor |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | MCS | Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Atmosphere, Color, Dust, Haze, Infrared, Movie, Thermal | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2018-08-06 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22546 | |
| Identifier | PIA22546 | |
