
|
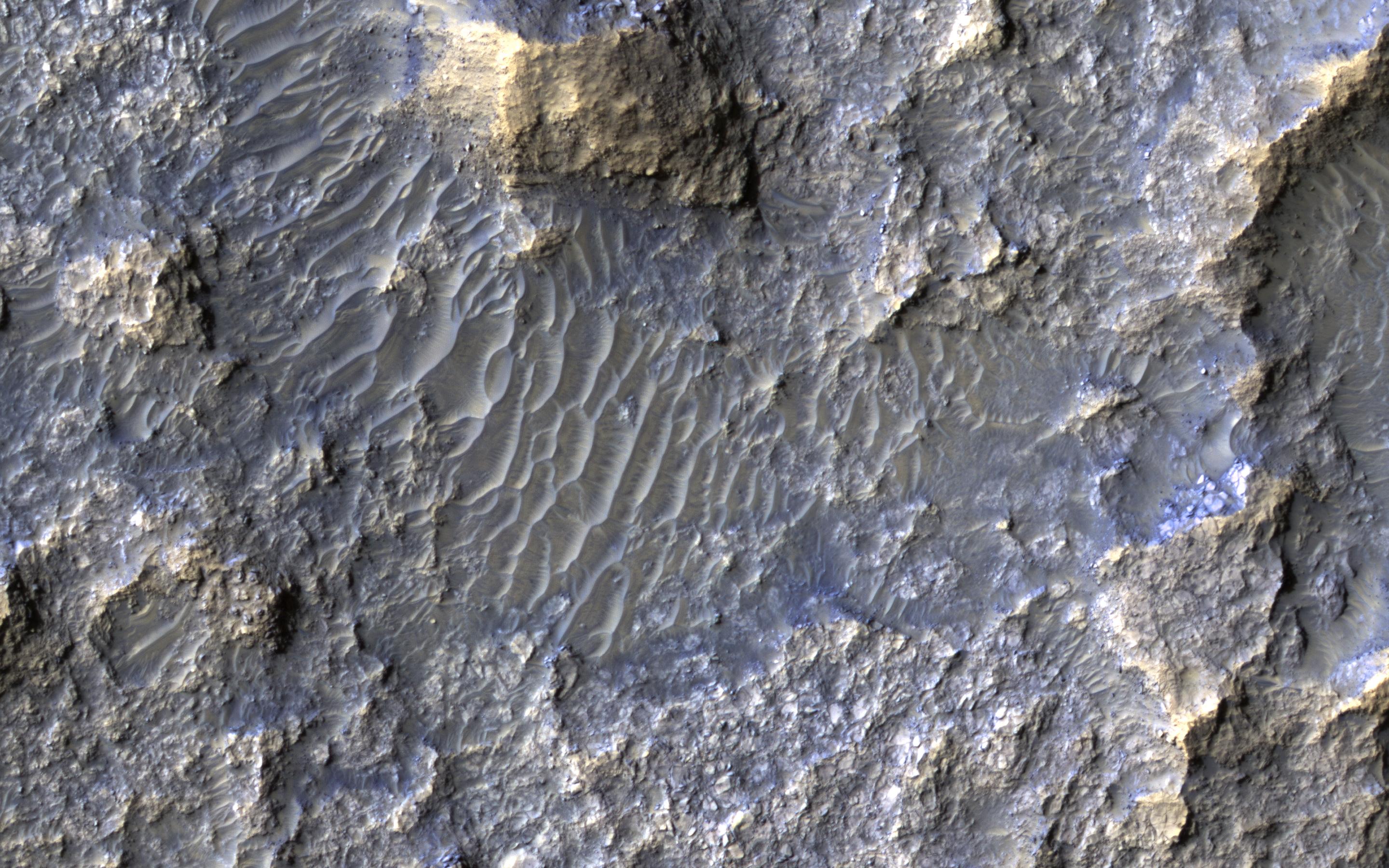
Bedforms and Bedrock
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (2880 x 1800) (815.1 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (2880 x 1800) (15.6 MB)
Caption:
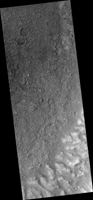
Map Projected Browse Image
Click on image for larger version
In this Context Camera image in Terra Cimmeria , we see a 30-kilometer diameter crater, filled-in with materials that created bedrock, and through subsequent erosion, wind-driven particles.
There is a ring of exposed light-toned bedrock at the base of the crater wall. This distinctive ring suggests high winds climbing up the crater wall slope may be responsible for the erosion and the extent of bedrock exposure we see. A close-up on the southeastern part of these deposits shows a mound of bedrock with beautiful color contrasts . The variation in color represents diverse minerals in the rock.
There is also a small degraded crater (about 300-meter diameter) to the left of the exposed bedrock. Fine-grained materials trapped inside the crater appear as wind-driven ripples or small dune-forms.
The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25.3 centimeters (10.0 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 76 centimeters (29.9 inches) across are resolved.] North is up.
Background Info:
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Crater, Dune, Map | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2018-10-01 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22782 | |
| Identifier | PIA22782 | |
