|
Voyager 2 CRS Data
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (1920 x 1080) (197.1 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (1920 x 1080) (538.3 kB)
Caption:
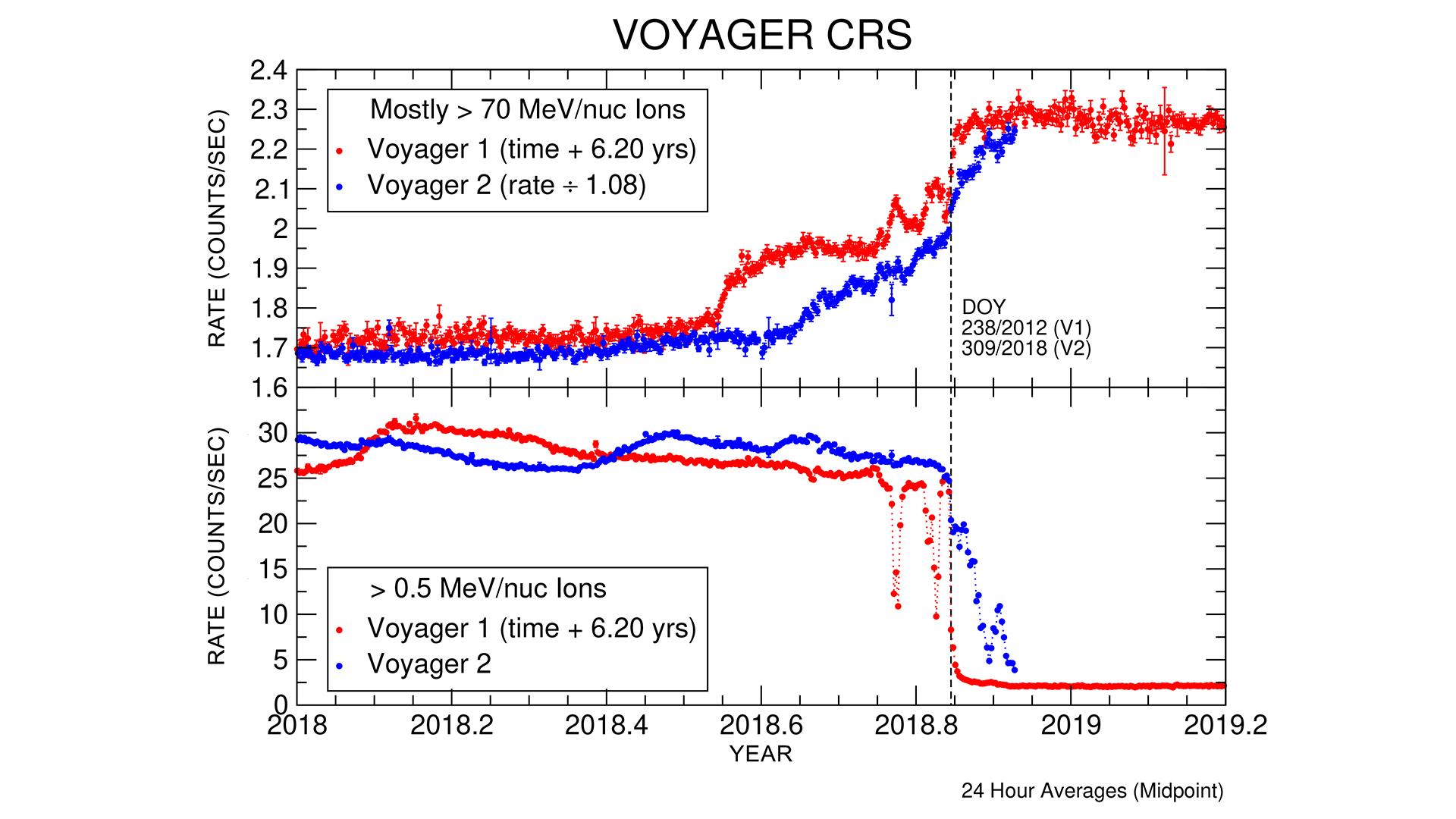
These graphs compare data from identical instruments onboard NASA's Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft as they each exited the heliosphere. Voyager 1 exited in 2012, and Voyager 2 exited in 2018. The cosmic ray subsystem (CRS) measures the rate of energetic particles hitting the radiation detector on the instrument. The top graph shows high energy particles (called cosmic rays) that originate outside the heliosphere. The CRS instruments on both spacecraft observed similar, but not identical, increases in the cosmic ray rate as they both crossed the heliopause (the outer edge of the heliosphere). The lower graph shows slightly lower energy particles that originate inside the heliosphere. Both spacecraft detected a similar but not identical decrease in these lower energy particles when they crossed the heliopause and immediately after.
Background Info:
The Voyager spacecraft were built by JPL, which continues to operate both. JPL is a division of Caltech in Pasadena. California. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington. For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit https://www.nasa.gov/voyager and https://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Heliosphere | |
| System | Solar System | |
| Target Type | Heliosphere | |
| Mission | Voyager | |
| Instrument Host | Voyager 1 | Voyager 2 |
| Host Type | Flyby Spacecraft | |
| Instrument | Cosmic Ray Subsystem (CRS) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2018-12-10 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22916 | |
| Identifier | PIA22916 | |
