|
Voyager 2: Hello Interstellar Space, Goodbye Heliosphere
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (3840 x 2160) (633.8 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (3840 x 2160) (8.9 MB)
Caption:
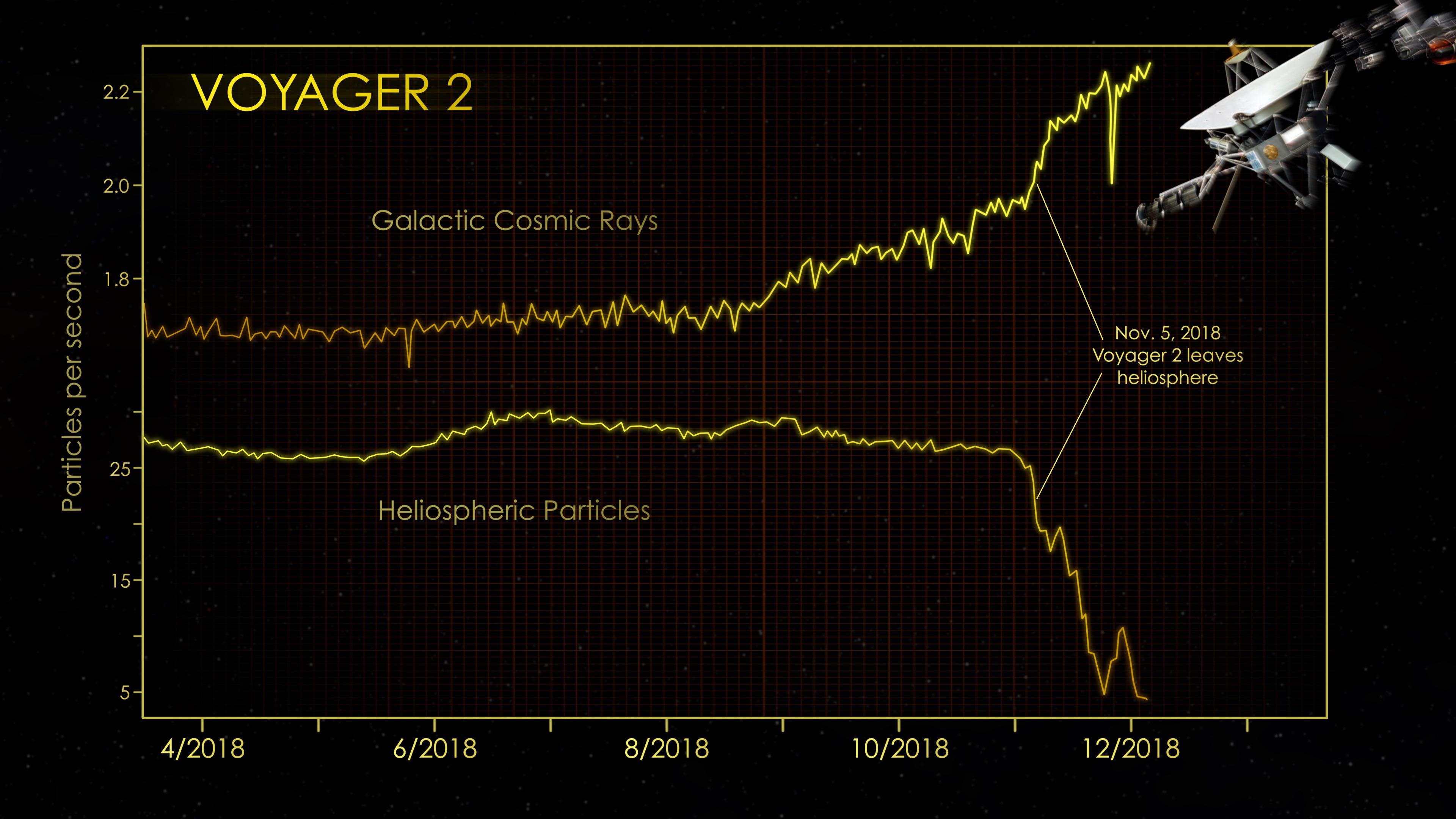
At the end of 2018, the cosmic ray subsystem (CRS) aboard NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft provided evidence that Voyager 2 had left the heliosphere (the plasma bubble the Sun blows around itself). There were steep drops in the rate at which particles that originate inside the heliosphere hit the instrument's radiation detector. At the same time, there were significant increases in the rate at which particles that originate outside our heliosphere (also known as galactic cosmic rays) hit the detector.
The graphs show data from Voyager 2's CRS, which averages the number of particle hits over a six-hour block of time. CRS detects both lower-energy particles that originate inside the heliosphere (greater than 0.5 MeV) and higher-energy particles that originate farther out in the galaxy (greater than 70 MeV).
Background Info:
The Voyager spacecraft were built by JPL, which continues to operate both. JPL is a division of Caltech in Pasadena. California. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington. For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit https://www.nasa.gov/voyager and https://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Heliosphere | |
| System | Solar System | |
| Target Type | Heliosphere | |
| Mission | Voyager | |
| Instrument Host | Voyager 2 | |
| Host Type | Flyby Spacecraft | |
| Instrument | Cosmic Ray Subsystem (CRS) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2018-12-10 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/GSFC | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22924 | |
| Identifier | PIA22924 | |
