|
Enceladus Organics on Grains of Ice (Illustration)
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (6300 x 6725) (1.9 MB)
- Full-Res TIFF (6300 x 6725) (38.2 MB)
Caption:
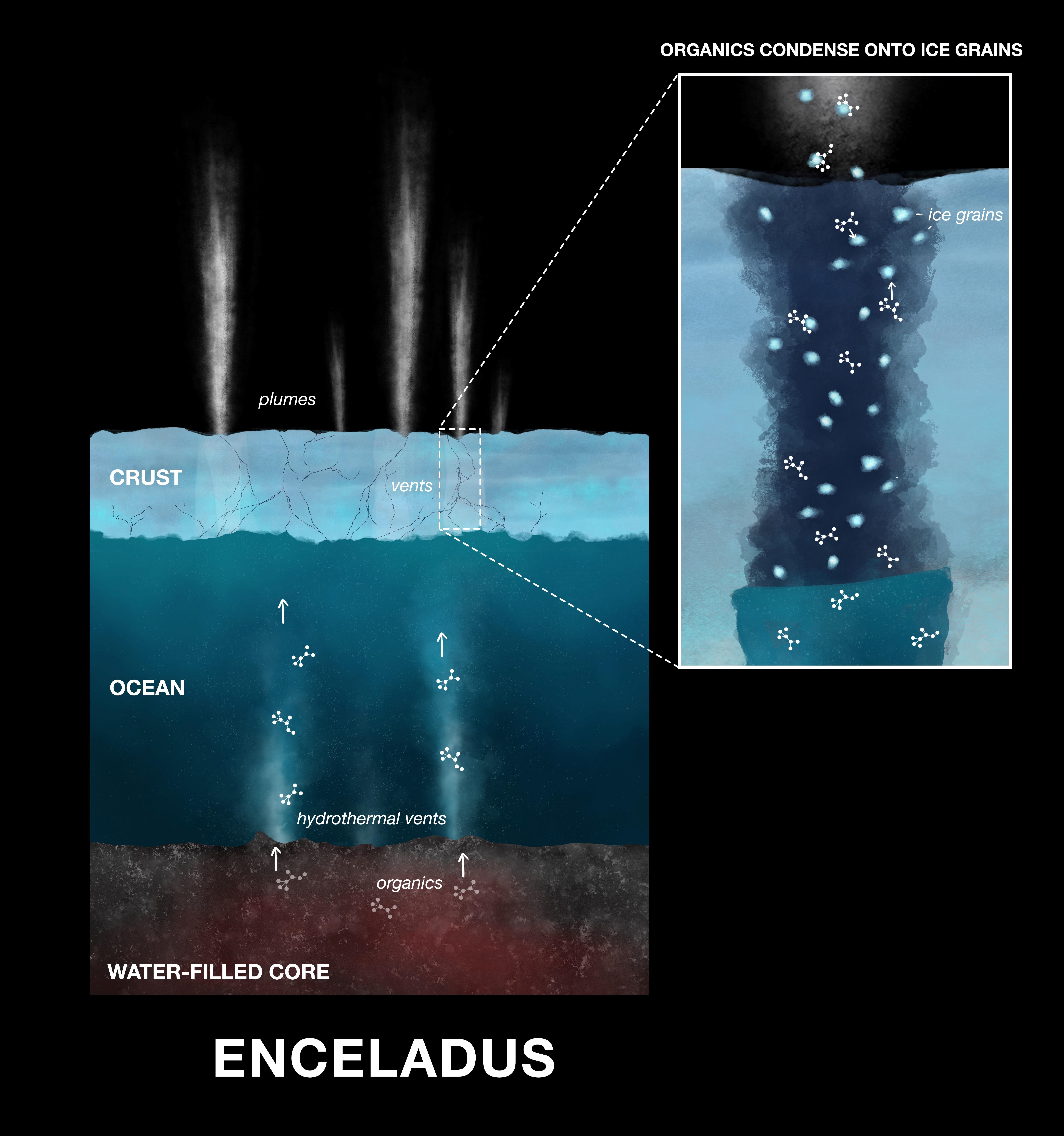
This illustration shows how newly discovered organic compounds — the ingredients of amino acids — were detected by NASA's Cassini spacecraft in the ice grains emitted from Saturn's moon Enceladus. Powerful hydrothermal vents eject material from Enceladus' core into the moon's massive subsurface ocean. After mixing with the water, the material is released into space as water vapor and ice grains. Condensed onto the ice grains are nitrogen- and oxygen-bearing organic compounds.
On Earth hydrothermal vents on the ocean floor provide the energy that fuels reactions that produce amino acids, the building blocks of life. Scientists believe Enceladus' hydrothermal vents may operate in the same way, supplying energy that leads to the production of amino acids.
Background Info:
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit https://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov and https://www.nasa.gov/cassini .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Enceladus | |
| System | Saturn | |
| Target Type | Satellite | |
| Mission | Cassini-Huygens | |
| Instrument Host | Cassini Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | ||
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Thermal, Water | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2019-10-02 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23173 | |
| Identifier | PIA23173 | |
