
|
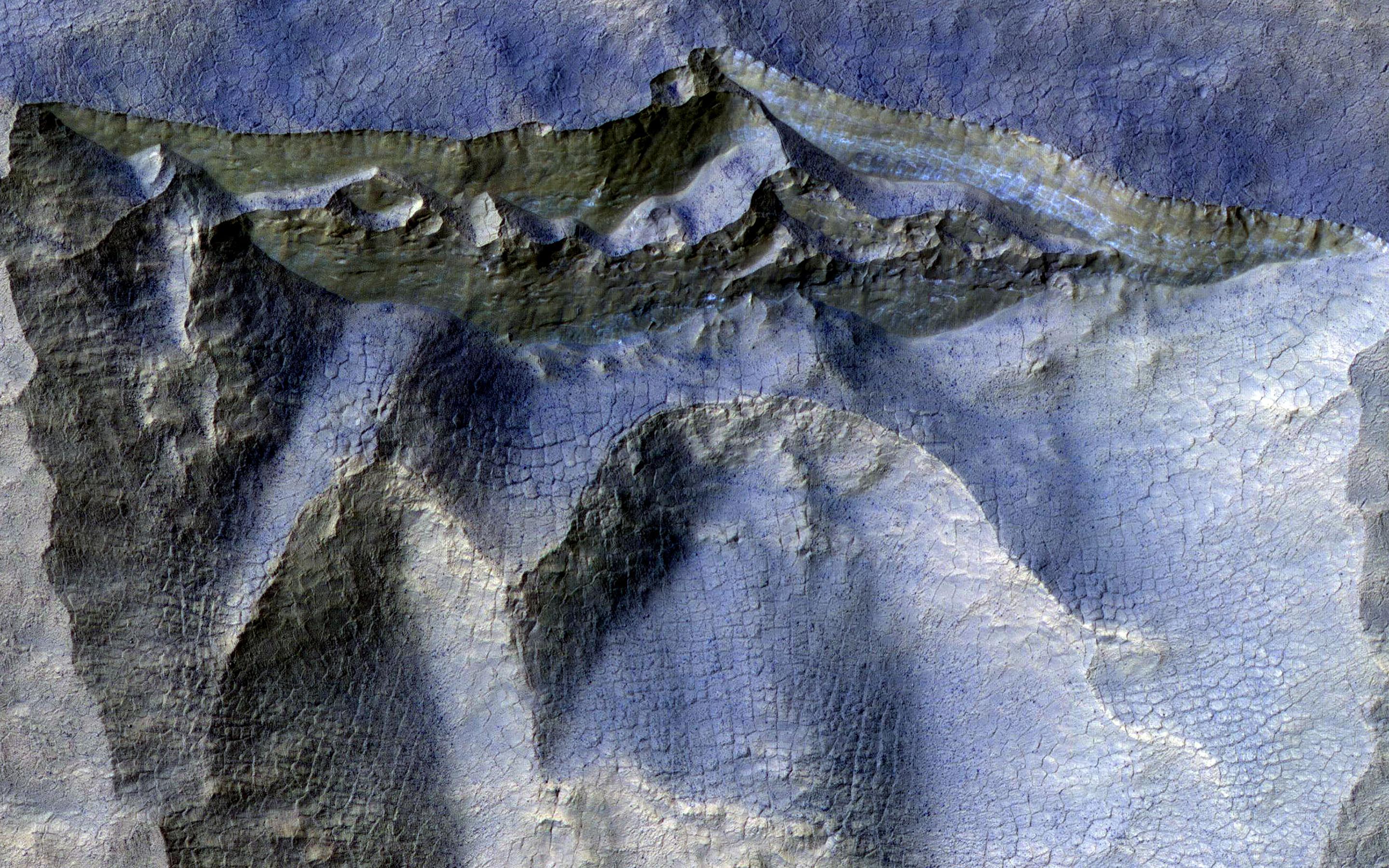
Cliffs in Ancient Ice
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (2880 x 1800) (1.1 MB)
- Full-Res TIFF (2880 x 1800) (15.6 MB)
Caption:
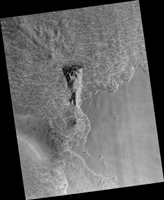
Map Projected Browse Image
Click on image for larger version
Scientists have come to realize that, just below the surface, about one third of Mars is covered in ice. We study this ice to learn about Mars' ancient climate and astronauts' future water supplies.
Sometimes we see the buried ice because cliffs form like the one in this image. On the brownish, dusty cliff wall, the faint light-blue-colored ice shows through . Some of these cliffs change before our eyes and boulders of ice can tumble downhill. We take repeat images of these scenes to check for changes like this.
The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. (The original image scale is 25.1 centimeters [9.9 inches] per pixel [with 1 x 1 binning]; objects on the order of 75 centimeters [29.5 inches] across are resolved.) North is up.
Background Info:
The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Dust, Map, Rotation, Water | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2020-10-12 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24147 | |
| Identifier | PIA24147 | |
