|
Radar Observations of Asteroid 4660 Nereus
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (3093 x 1963) (1.4 MB)
- Full-Res TIFF (3093 x 1963) (4.1 MB)
Caption:
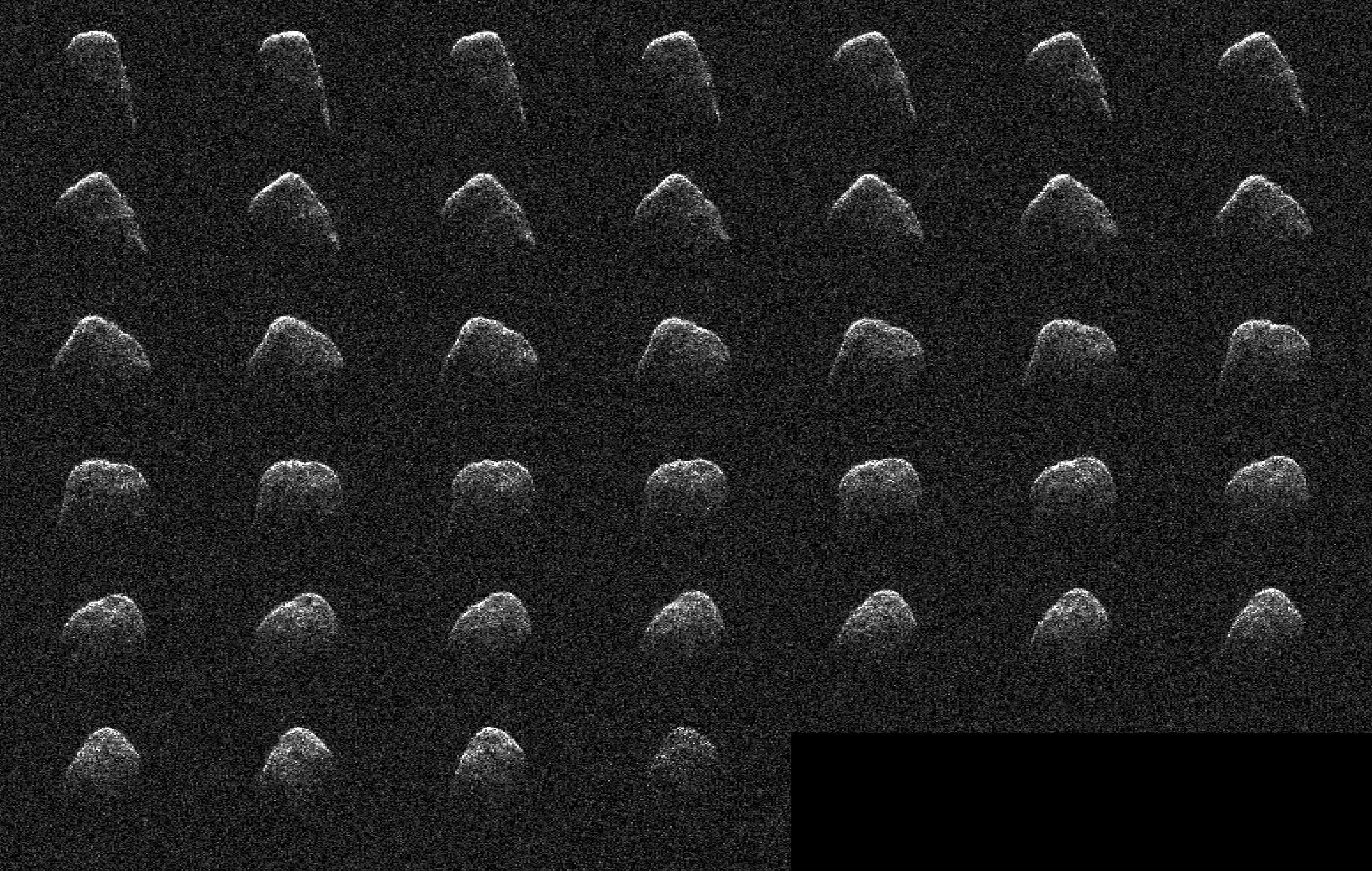
These images and animation represent NASA radar observations of 4660 Nereus on Dec. 10, 2021, before the asteroid's close approach on Dec. 11, when it came within 2.5 million miles (4 million kilometers) of Earth. Using the 70-meter radio antenna at the Deep Space Network's Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex near Barstow, California, scientists from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory acquired the most detailed radar images of the nearly 1,100-foot-wide (330-meter-wide) near-Earth asteroid since its discovery almost four decades earlier. Nereus' orbit is very well known and the asteroid does not pose a threat to Earth.
During the asteroid's close approach, an image resolution of about 12.3 feet (3.75 meters) per pixel was possible, revealing surface features such as potential boulders and craters, plus ridges and other topography. Asteroid Nereus' previous approach in 2002 was near enough to Earth to reveal the asteroid's size and overall shape, but too distant to show surface features. The new observations will also help scientists better understand the asteroid's shape and rotation while providing them new data to further refine its orbital path around the Sun.
Nereus belongs to the relatively rare E-type asteroid family that exhibits very unusual radar scattering properties. It's thought that this may be caused by asteroids of this type having particularly rough terrain. Also, E-type asteroids are optically bright, sometimes reflecting as much as 50% of the sunlight that hits their surface. Typical S-type asteroids reflect about 15%, whereas dark C-type asteroids reflect only a few percent. It's thought that E-class asteroids may be the source of very rare Aubrite meteorites and are composed of comparatively bright material.
The 2021 close approach was the best opportunity for radar imaging of Nereus until 2060, when the asteroid will approach within 750,000 miles (1.2 million kilometers) of Earth, only three times the Earth-Moon distance. At that time, Nereus will be an easy target for small telescopes and possibly even powerful binoculars.
Nereus – named after a sea god from Greek mythology – was discovered in 1982 by Eleanor "Glo" Helin as part of the JPL Palomar Planet-Crossing Asteroid Survey.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | 4660 Nereus | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Asteroid | |
| Mission | Deep Space Network (DSN) | |
| Instrument Host | Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex (GDSCC) | |
| Host Type | Ground-Based Observatory | |
| Instrument | Goldstone Solar System Radar | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Crater, Grayscale, Radar, Radio, Rotation | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2022-01-10 | |
| Date in Caption | 2021-12-10 | |
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24566 | |
| Identifier | PIA24566 | |
