|
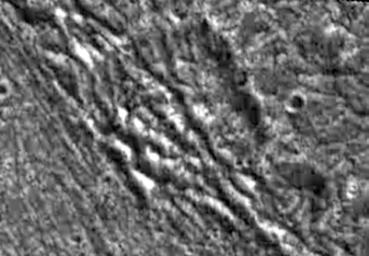
Fractured Craters on Ganymede
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (400 x 278) (23.0 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (400 x 278) (122.6 kB)
Caption:
Two highly fractured craters are visible in this high resolution image of Jupiter's moon, Ganymede. NASA's Galileo spacecraft imaged this region as it passed Ganymede during its second orbit through the Jovian system. North is to the top of the picture and the sun illuminates the surface from the southeast. The two craters in the center of the image lie in the ancient dark terrain of Marius Regio, at 40 degrees latitude and 201 degrees longitude, at the border of a region of bright grooved terrain known as Byblus Sulcus (the eastern portion of which is visible on the left of this image). Pervasive fracturing has occurred in this area that has completely disrupted these craters and destroyed their southern and western walls. Such intense fracturing has occurred over much of Ganymede's surface and has commonly destroyed older features. The image covers an area approximately 26 kilometers (16 miles) by 18 kilometers (11 miles) across at a resolution of 86 meters (287 feet) per picture element. The image was taken on September 6, 1996 by the solid state imaging (CCD) system on NASA's Galileo spacecraft.
Background Info:
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, CA manages the Galileo mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, DC. JPL is an operating division of California Institute of Technology (Caltech).
This image and other images and data received from Galileo are posted on the World Wide Web, on the Galileo mission home page at URL http://galileo.jpl.nasa.gov.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Ganymede | |
| System | Jupiter | |
| Target Type | Satellite | |
| Mission | Galileo | |
| Instrument Host | Galileo Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | Solid-State Imaging (SSI) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Crater, Grayscale | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 1997-11-25 | |
| Date in Caption | 1996-09-06 | |
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL/Brown University | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01089 | |
| Identifier | PIA01089 | |
