|
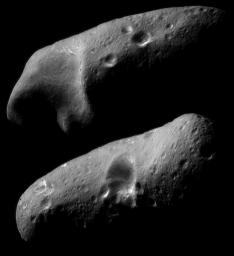
Eros’ Eastern and Western Hemispheres
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (742 x 812) (45.9 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (742 x 812) (267.9 kB)
Caption:
On February 23, 2000, the NEAR spacecraft obtained a sequence of image mosaics showing Eros' surface as the asteroid rotated under the spacecraft. At that time the range to the surface was approximately 355 kilometers (220 miles). These two mosaics, part of that sequence, show the stark beauty of the two opposite hemispheres. The smallest detail visible is 35 meters (120 feet) across. The top mosaic shows wavy brightness banding exposed in the interior walls of the saddle. In the bottom mosaic, similar banding is visible in one of the craters near the limb at left. To the right, the angle of the illumination accentuates the quasi-linear troughs near the terminator.
Successful firing of NEAR's thrusters yesterday, February 24, placed the spacecraft on course for insertion into the next lower orbit, at a 200 kilometer (120 mile) altitude. Images from that orbit, commencing in early March, will have nearly twice the spatial resolution of data returned so far.
Background Info:
Built and managed by The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, Maryland, NEAR was the first spacecraft launched in NASA's Discovery Program of low-cost, small-scale planetary missions. See the NEAR web page at http://near.jhuapl.edu/ for more details.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | 433 Eros | |
| System | Near Earth Objects | |
| Target Type | Asteroid | |
| Mission | NEAR Shoemaker | |
| Instrument Host | NEAR Shoemaker | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | Multi-Spectral Imager (MSI) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Crater, Grayscale, Rotation | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2000-05-07 | |
| Date in Caption | 2000-02-23 | |
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL/JHUAPL | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02474 | |
| Identifier | PIA02474 | |
