|
An Enigmatic Feature in Athabasca Lava Flows
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (2880 x 1800) (552.5 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (2880 x 1800) (5.2 MB)
Caption:

Map Projected Browse Image
Click on the image for larger version
What is this enigmatic landform?
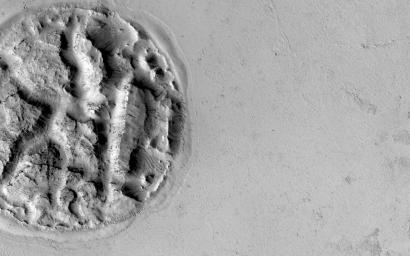
The circular feature is nearly 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) wide. It looks like a circular island surrounded by a "sea" of smooth-looking lava flows. The Athabasca region contains some of the youngest lava flows on Mars. Therefore, it is highly possible that volcanism played a role in creating this feature.
Perhaps lava has intruded underneath this mound and pushed it up from beneath. It looks as if material is missing from the mound, so it is also possible that there was a significant amount of ice in the mound that was driven out by the heat of the lava. There are an array of features like this in the region that continue to puzzle scientists.
We hope that close inspection of this HiRISE image, and others around it, will provide some clues regarding its formation.
Background Info:
HiRISE is one of six instruments on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Grayscale, Map, Volcano | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2014-12-03 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18932 | |
| Identifier | PIA18932 | |
