|
Big Boulders
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (1435 x 1054) (114.6 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (1435 x 1054) (1.5 MB)
Caption:
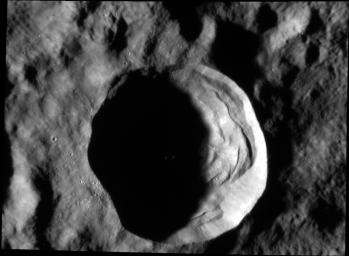
On Mercury, craters larger than approximately 10-12 km display a complex morphology , with slump terraces and central peaks, as compared to smaller bowl-shaped craters. At this complex crater, nearly 20 km in diameter, boulders created by the impact event can be seen outside the southwest rim and within the crater interior. The largest boulder observed here is around 180 m (590 feet) across! For comparison with humans for scale, check out the lunar House Rock at the Apollo 16 site, which is (only) 24 meters across.
Date acquired:
January 24, 2015
Image Mission Elapsed Time (MET):
64441328
Image ID:
7855678
Instrument:
Narrow Angle Camera (NAC) of the Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS)
Center Latitude:
-2.66°
Center Longitude:
83.54° E
Resolution:
26 meters/pixel
Scale:
This crater is approximately 19.5 km (12.1 miles) in diameter
Incidence Angle:
82.8°
Emission Angle:
43.0°
Phase Angle:
39.8°
Background Info:
The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. During the first two years of orbital operations, MESSENGER acquired over 150,000 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is capable of continuing orbital operations until early 2015.
For information regarding the use of images, see the MESSENGER image use policy .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mercury | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | MESSENGER | |
| Instrument Host | MESSENGER | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) | |
| Detector | Narrow Angle Camera (NAC) | |
| Extra Keywords | Crater, Grayscale, Impact, Radio | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2015-02-11 | |
| Date in Caption | 2015-01-24 | |
| Image Credit | NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19202 | |
| Identifier | PIA19202 | |
