
|
Erosion of the Edge of the South Polar Layered Deposits
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (2699 x 2024) (985.1 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (2699 x 2024) (16.4 MB)
Caption:
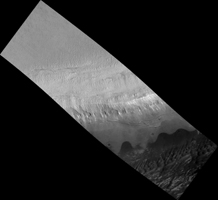
Map Projected Browse Image
Click on the image for larger version
This image is an oblique view from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter of the sloping edge of the stack of icy layers over the South Pole has some interesting morphologies.
The slope appears to be eroding from a combination of landslides, block falls, and sublimation. The bright icy exposure in the larger landslide scar (upper right) suggests that this was a relatively recent event.
Small-scale textures over the scene are due to both blowing wind and the thermal expansion and contraction of shallow ice.
This is a stereo pair with ESP_013026_1080 .
The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 57.1 centimeters (22.5 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 171 centimeters (67.3 inches) across are resolved. North is up.
Background Info:
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colo. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Map, Thermal | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2017-05-22 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21637 | |
| Identifier | PIA21637 | |
