|
Investigating Mars: Arsia Mons
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (1294 x 2770) (503.7 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (1294 x 2770) (2.9 MB)
Caption:
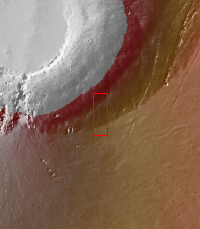
This image shows part of the southeastern flank of Arsia Mons, including the flat lying flows around the base of the volcano. These flows are located at the bottom of the image. Numerous small lava channels are visible aligned sub-parallel to the base of the volcano. Several narrow, lobate flows show the downslope direction from the top left of the image towards the bottom right. Running against this elevation change are large paired faults called graben. Graben form by faults that have allowed the material between them to "slide" down. The resultant topography is a linear depression. None of the lobate flows enter and then run along the fault valley, indicating that the faulting occurred after the lava flows.
Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 270 miles (450km) in diameter, almost 12 miles (20km) high, and the summit caldera is 72 miles (120km) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter. A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse. The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth.
Orbit Number: 17691 Latitude: -11.2622 Longitude: 241 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-12-09 23:06
Background Info:
The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images!
Please see the THEMIS Data Citation Note for details on crediting THEMIS images.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the 2001 Mars Odyssey mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) was developed by Arizona State University, Tempe, in collaboration with Raytheon Santa Barbara Remote Sensing. The THEMIS investigation is led by Dr. Philip Christensen at Arizona State University. Lockheed Martin Astronautics, Denver, is the prime contractor for the Odyssey project, and developed and built the orbiter. Mission operations are conducted jointly from Lockheed Martin and from JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | 2001 Mars Odyssey | Mariner |
| Instrument Host | Mars Odyssey | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | Flyby Spacecraft |
| Instrument | Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Crater, Dune, Grayscale, Infrared, Mountain, Thermal, Volcano, Water | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2017-12-29 | |
| Date in Caption | 2005-12-09 | |
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22154 | |
| Identifier | PIA22154 | |