
|
Icy Layers in Craters
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (4500 x 3000) (1.7 MB)
- Full-Res TIFF (4500 x 3000) (40.5 MB)
Caption:
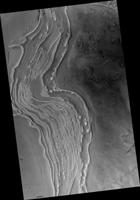
Map Projected Browse Image
Click on the image for larger version
In this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Rover (MRO) we can see the edge of a mound of ice in one of these mid-latitude craters. Some of it has already been removed, so we can see layering that used to be in the crater's interior. Scientists use ice deposits like these to figure out how the climate has changed on Mars. Another upside of recognizing this ice is that future astronauts will have plenty of drinking water.
Scientists now realize that ice is very common on the Martian surface. It often fills up craters and valleys in the mid-latitudes in older climates, although when it's covered in dust it can be hard to recognize. Today the climate on Mars makes this ice unstable and some of it has evaporated away.
The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 59.6 centimeters (23.5 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 179 centimeters (70.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up.
Background Info:
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Crater, Dust, Map, Water | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2018-02-20 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22255 | |
| Identifier | PIA22255 | |
