|
Spring Sprouts on Mars
- Click the image above for a larger view
- Full-Res JPEG (2880 x 1800) (1.1 MB)
- Full-Res TIFF (2880 x 1800) (15.6 MB)
Caption:

Map Projected Browse Image
Click on image for larger version
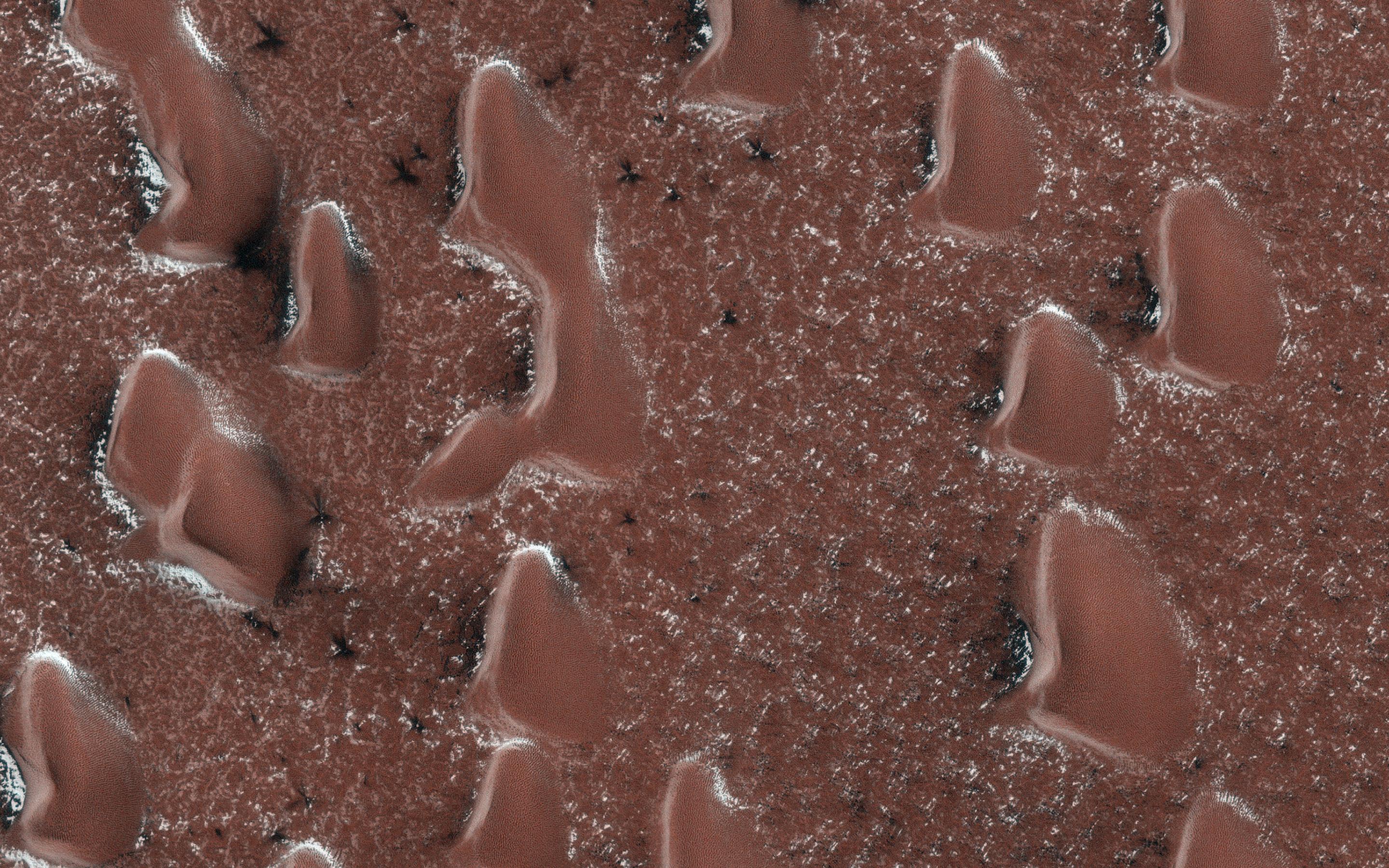
The sun is rising in Mars' Northern Hemisphere, and spring activity is starting as the seasonal polar cap begins to sublimate (going from ice directly to gas). A layer of dry ice covers the sand dunes in this image.
Gas jets sprout through the ice layer carrying dust and sand from the surface, showing up as dark fans. At this time in early Martian spring, the fans are visible between the sand dunes. The ground between the dunes is on the scale of tens of centimeters, and ice in places where the sun hits more directly will thin fastest, releasing the jets. Later, the ice over and around the dunes will rupture and more fans will appear on the dunes.
The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. (The original image scale is 63.4 centimeters [25.0 inches] per pixel [with 2 x 2 binning]; objects on the order of 190 centimeters [74.8 inches] across are resolved.) North is up.
Background Info:
The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mars | |
| System | ||
| Target Type | Planet | |
| Mission | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) | |
| Instrument Host | Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) | |
| Detector | ||
| Extra Keywords | Color, Dune, Dust, Map | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2021-01-29 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24390 | |
| Identifier | PIA24390 | |
