|
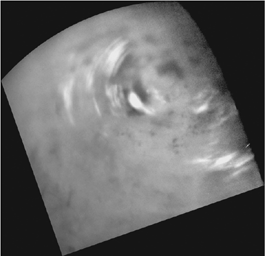
Northern Clouds in Motion
- Click the image above for a larger view
 Movie Download Options
Movie Download Options- Full-Res JPEG (650 x 629) (30.1 kB)
- Full-Res TIFF (650 x 629) (409.5 kB)
Caption:
Click on the image for the movie
Clouds move above Titan's large methane lakes and seas near the moon's north pole in this movie made from images taken by NASA's Cassini spacecraft. For a view of these same clouds re-projected to a different perspective, see PIA12811 which adds a fifth frame with labels for Titan's lakes and seas.
Methane clouds in the troposphere, the lowest part of the atmosphere, appear white here and can be seen moving east over several of Titan's large northern lakes. The darkest areas are lakes and seas of liquid methane, identifiable because they have a low albedo, meaning they do not reflect much light. (The difference in brightness and darkness on the surface here indicates a difference in composition.) The clouds seen near lakes and seas suggest that Titan (5,150 kilometers or 3,200 miles across) may have "lake-effect" clouds created by weather systems over large bodies of liquid. However, without earlier observations to show the clouds did not originate west of the large sea Kraken Mare, scientists can't determine conclusively if these clouds are "lake-effect" clouds.
Near the beginning of the animation, a particularly large cloud can be seen directly over and east of Titan's huge sea, Kraken Mare, near the center top of the frame. If full, Kraken Mare, at 400,000 square kilometers (154,000 square miles), would be almost five times the size of North America's Lake Superior.
Even if these clouds are not directly connected to the lakes and seas, scientists think that frequent detections of clouds at high northern latitudes since 2007 are related to the abundant availability of methane at the surface in this region.
The four images used in this animation were taken over a period of about 24 hours from Sept. 22 to 23, 2009.
These images were re-projected, and the view is centered on terrain at 49 degrees north latitude, 179 degrees west longitude. The north pole is near the upper right. The clouds are visible above terrain at about 60 to 82 degrees north latitude, 220 to 260 degrees west longitude. Scientists calculate wind speeds from about 0.5 to 10 meters per second (1 to 22 miles per hour), based on tracking of individual cloud features in these images.
Other Cassini observations of clouds in Titan's southern latitudes provide evidence of a seasonal shift of Titan's weather systems to low latitudes from higher, south polar latitudes following the August 2009 equinox in the Saturnian system. See PIA12810 and PIA12813 to learn more about the changes in Titan's southern hemisphere.
These images were taken with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera using a spectral filter sensitive to wavelengths of near-infrared light centered at 938 nanometers. The view was obtained at a range of distances from approximately 406,000 kilometers (252,000 miles) to 796,000 kilometers (494,000 miles) from Titan. Scale is about 2 kilometers (1 miles) per pixel in these re-projected images.
Background Info:
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging team is based at the Space Science Institute, Boulder, Colo.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov . The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org .
Cataloging Keywords:
| Name | Value | Additional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Titan | |
| System | Saturn | |
| Target Type | Satellite | |
| Mission | Cassini-Huygens | |
| Instrument Host | Cassini Orbiter | |
| Host Type | Orbiter | |
| Instrument | Imaging Science Subsystem (ISS) | |
| Detector | Narrow Angle Camera | |
| Extra Keywords | Atmosphere, Grayscale, Infrared, Methane, Movie, Visual | |
| Acquisition Date | ||
| Release Date | 2011-03-17 | |
| Date in Caption | ||
| Image Credit | NASA/JPL/Space Science Institute | |
| Source | photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12812 | |
| Identifier | PIA12812 | |
